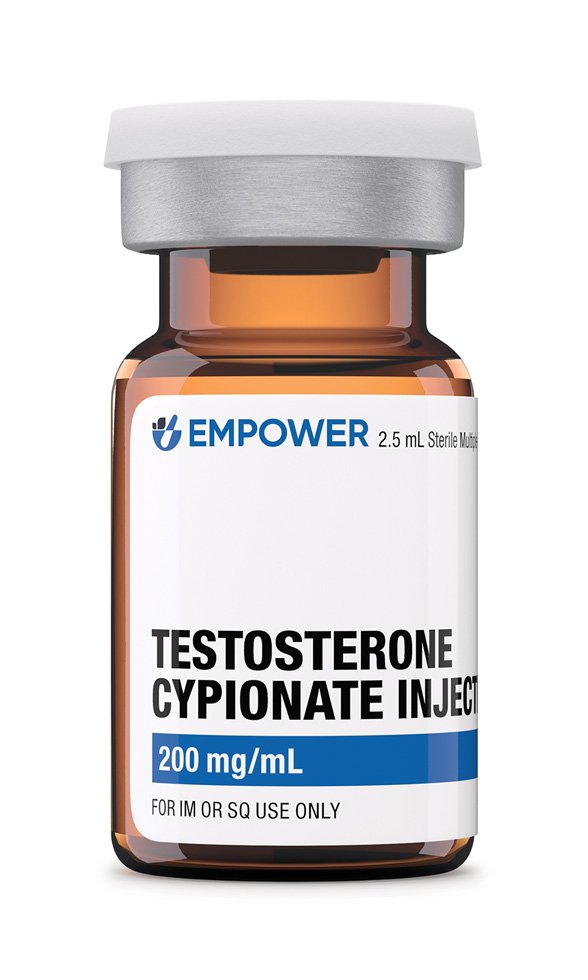
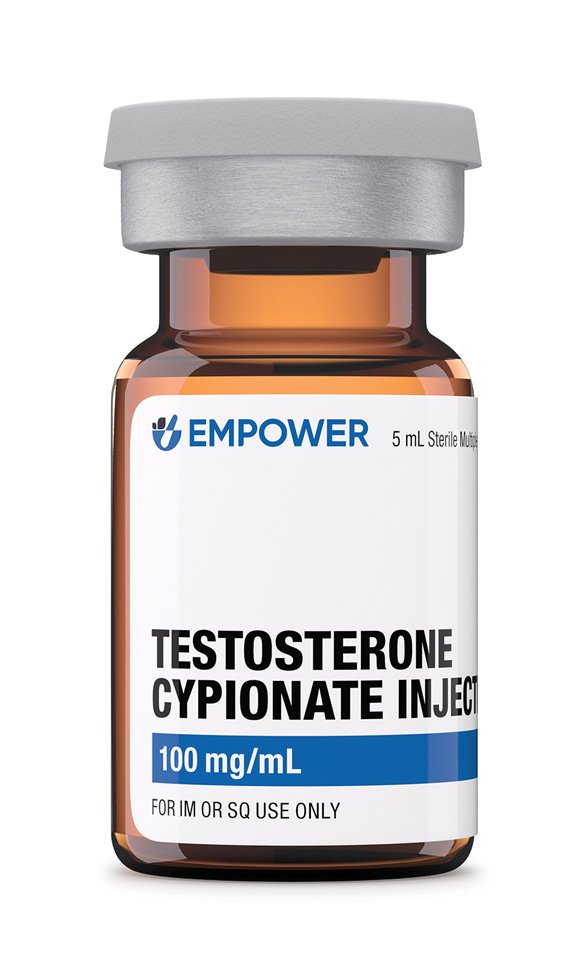
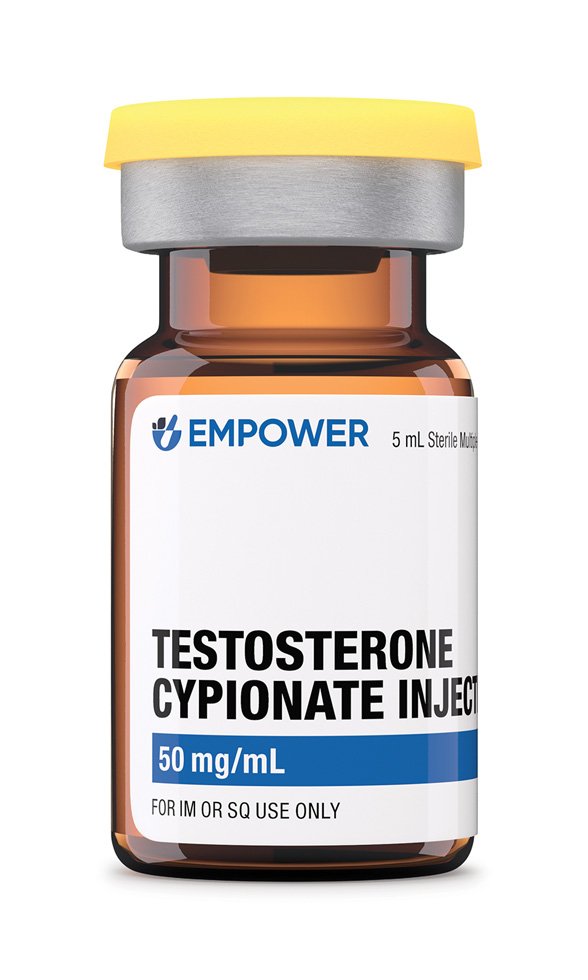
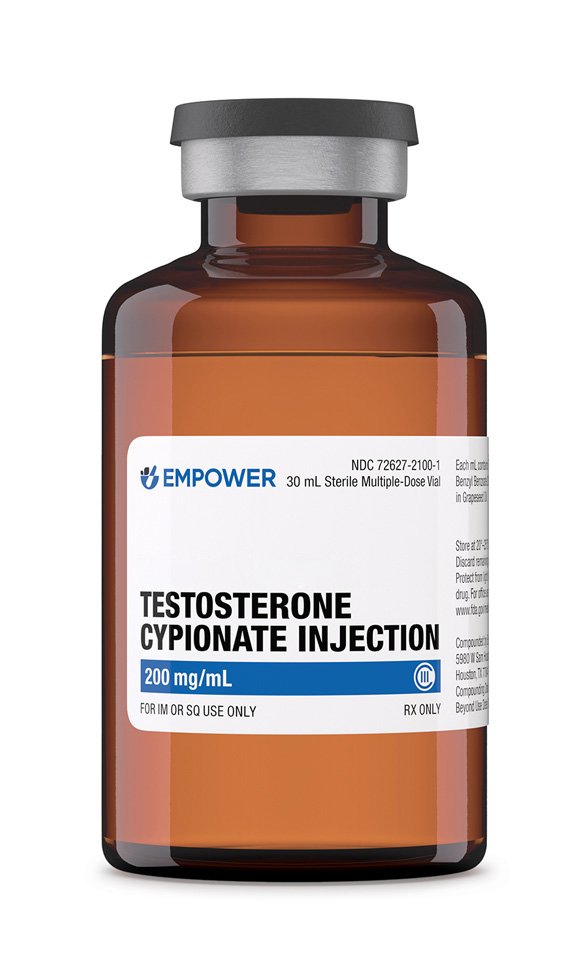
Testosterone cypionate is a long-acting esterified form of the endogenous androgen testosterone formulated in grapeseed oil for intramuscular administration; it is compounded in concentrations ranging from 20 mg/mL to 200 mg/mL across 1 mL, 2·5 mL, 5 mL, 10 mL and 30 mL multi-dose vials, allowing prescribers to match dose and vial size precisely to patient requirements.
As an individualized preparation produced under sections 503A or 503B of the U.S. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, each batch may be tailored for a single named patient or manufactured in larger lots for office use, yet in both scenarios the formulation must meet pharmaceutical quality standards for sterility, potency and particulate control.
Clinically, compounded testosterone cypionate is prescribed for adult males with confirmed hypogonadism who exhibit symptoms such as reduced muscle mass, diminished libido, erectile dysfunction, fatigue or mood disturbance and in whom morning serum testosterone levels on two separate days fall below the young-adult reference range.
Because the product is an anabolic-androgenic steroid classified as a Schedule III controlled substance it may only be dispensed pursuant to a valid prescription, must be stored securely and is subject to state and federal monitoring programs aimed at preventing diversion and misuse.
The compounded nature of the formulation means inactive components, usually limited to grapeseed oil and possibly a bacteriostatic agent, can be adjusted to address allergies or other patient-specific considerations, thereby offering flexibility beyond what is available with a single commercial brand while still requiring physician oversight and periodic laboratory monitoring to ensure both efficacy and safety.
Typical initiation for primary or secondary hypogonadism in adult males is 100 mg to 200 mg injected intramuscularly every two weeks, though some clinicians favour 50 mg weekly to minimise peak-trough fluctuations; serum testosterone is rechecked after two injection intervals and the dose or frequency is adjusted to maintain trough levels in the mid-normal adult range while avoiding supraphysiologic peaks.
Deep intramuscular administration into the gluteal muscle using a 22-gauge needle is recommended, and patients who self-inject must be trained in aseptic technique, site rotation and safe sharps disposal to reduce infection and tissue-injury risk.
After deep intramuscular injection the lipophilic ester diffuses slowly from the oil depot, undergoes enzymatic cleavage to free testosterone and enters the systemic circulation, where roughly 98 % is reversibly bound to sex-hormone-binding globulin and albumin while the unbound fraction translocates across cell membranes to activate androgen receptors .
Ligand-bound androgen receptor complexes dimerize, migrate to the nucleus and modulate transcription of target genes governing protein synthesis, erythropoiesis, bone mineralization, libido and secondary sexual characteristics; some intracellular testosterone is converted by 5-alpha reductase to the more potent dihydrotestosterone, whereas in adipose tissue a proportion aromatizes to estradiol, supporting skeletal maturation and feedback control of gonadotropins .
Administration therefore restores physiologic androgen levels, suppresses hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone and pituitary luteinizing hormone, stabilizes nitrogen balance, increases lean body mass and may improve mood and sexual function, yet prolonged suppression of intratesticular testosterone can reduce spermatogenesis, underscoring the need for careful dose titration and fertility counseling when indicated.
Testosterone cypionate is contraindicated in men with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate because exogenous androgens can stimulate androgen-dependent malignant tissue growth.
It must not be administered to patients with hypersensitivity to testosterone, grapeseed oil or any component of the formulation, or to women who are pregnant, could become pregnant or are breastfeeding owing to the risk of virilization and other fetal or neonatal harm.
Androgen therapy can potentiate the hypoglycaemic effect of insulin and oral antidiabetic agents, necessitating closer monitoring of fasting glucose and possible dose reductions when testosterone replacement is initiated in diabetic patients.
Concomitant use with oral anticoagulants such as warfarin may enhance anticoagulation and alter international normalised ratio values, so prothrombin time should be reviewed more frequently following dose changes of either drug.
Co-administration with glucocorticoids or adrenocorticotropic hormone may exacerbate fluid retention and oedema; similarly, potent CYP3A4 inhibitors could raise serum testosterone concentrations, whereas 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors counteract androgenic activity, highlighting the importance of comprehensive medication reconciliation at each visit.
Common adverse reactions include transient injection-site discomfort, acne, seborrhoea, increased body hair, mild fluid retention and elevations in haematocrit that may require dose reduction or therapeutic phlebotomy if haematocrit exceeds 54 %.
Prolonged therapy can unmask or exacerbate benign prostatic hyperplasia, raise prostate-specific antigen, worsen untreated obstructive sleep apnoea and is associated in some observational studies with a small but controversial increase in cardiovascular events, underlining the necessity for baseline and periodic monitoring of PSA, lipids and cardiovascular risk factors.
Exogenous testosterone is teratogenic, capable of inducing virilisation of a female fetus when administered during pregnancy; therefore the drug is absolutely contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant and exposure during gestation mandates immediate discontinuation and medical evaluation.
Because testosterone and its metabolites could be excreted into breast milk and might suppress lactation or adversely affect a nursing infant, therapy is likewise contraindicated during breastfeeding and should not be used in women for routine androgen replacement.
Store vials upright at controlled room temperature of 20 °C to 25 °C; protect from light by keeping the vial in its carton and never freeze the oil solution, as crystallisation or vial breakage can occur at sub-zero temperatures.